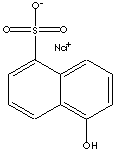
| Naphthols are either of two crystalline monohydric alcohols, derived from
naphthalene and belong to the phenol family. There are position isomers;
alpha-naphthol (also called 1-naphthol) is 1-hydroxynaphthalene and
beta-naphthol (also called 2-naphthol) is 2-hydroxynaphthalene. The compound
1-naphthol is made by heating 1-naphthalenesulfonic acid with caustic alkali or
by heating 1-naphthylamine with water under pressure. The compound 2-naphthol is
manufactured by fusing 2-naphthalenesulfonic acid with caustic soda. The
different positions provide various chemical structures which offer important
roles to each characteristic colours. Naphthols are slightly soluble in water
but readily soluble in short alcohols, ethers chlorinated solvents, and caustic
alkalis. They are used directly in making several dyes and are converted into
numerous corresponding amines, esters, ethers and carboxylic derivatives as well
as into numerous sulfo- and nitro-group substituted (mono-, di- and tri) naphthol
compounds. They find extensive applications in making dyes, pigments,
fluorescent whiteners, tanning
agents, antioxidants, and antiseptics. Naphthol structure is found as a ligand
in transition-metal catalysts particularly in the form of
binaphthol (binol) which is composed of two naphthol rings connected at one
carbon site on each ring. Optically active binol is widely used in asymmetric
synthesis of rearrangements, epoxidations, reductions.
Sulfonic acid is a compound with general formula RSO2OH, where R is an aliphatic
or aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a derivative of sulfuric acid (HOSO2OH) where an
OH has been replaced by a carbon group or a compound where a hydrogen atom has
been replaced by treatment with sulfuric acid; for example, benzene is converted
to benzenesulfonic acid (water-soluble). Sulfonic acid has a sulfur atom bonded
to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon and bonded also to three oxygen atoms, one of
which has been attached to a hydrogen atom. Sulfonic acid is acidic due to the
hydrogen atom, stronger than a carboxylic acid. Sulfonic acid is one of the most
important organo sulfur compounds in organic synthesis. Sulfonic acids are used
as catalysts in esterification, alkylation and condensation reactions.
Sulfonates are salts or esters of sulfonic acid. Sulfonic salts are soluble in
water. Sulfonic acid and its salts present in organic dyes provide useful
function of water solubility and or improve the washfastness of dyes due to
their capabiltity of binding more tightly to the fabric.
|